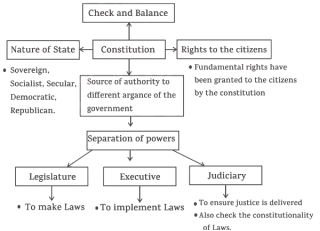
Constitution
It is the legal document which outlines the structure of the governance and also
it is the source of power to different organs of the government.
Constitution also provides the rights to the citizens. Therefore constitution is the
supreme law of land.
Constitution is the supreme law of land
• It means there is nothing above the constitution.
• Everything derives its power from the Constitution.
Different types of the Constitution
- Written Vs Unwritten Constitution
| Written | Unwritten |
| If there is a single codified document then it is called written constitution. Ex- Indian Constitution, U.S.A | It means the constitution has not been codified in a single document. Rather the governance of the country is done on the basis of laws, conventions, customes etc. Ex.- British, Israel |
2) Rigid & Flexible Constitution
| Rigid | Flexible |
| Which are very difficult to amend. Ex.- U.S.A | Which are very easy to amend.Ex.- British Constitution(because British parliament has wide powers) |
Note :- Indian Constitution is blend of rigidity & flexibility it means that Indian
constitution is neither rigid like U.S.A Constitution nor it is flexible like British
Constitution.
3) Unitary Vs Federal Constitution
| Unitary | Federal |
| There is no division of powers between the centre and the state.Ex.- British Constitution | Division of powers between the centre and the state. Ex.- U.S.A, Indian Constitution |
4) Secular Vs Theocratic Constitution
| Secular | Theocratic |
| The Constitution doesn’t declare any religion to be the official relegion of the country/state. Ex.- Indian | There will be official religion of the state/country. Ex.- Pakistan, Saudi-Arabia, Iran, Vetican City. |
Note :-
- The centre cam reorganise a state, but a state cannot reorganise the centre.
5) Parliamentary Vs Presidential System
| Parliamentary | Presidential |
| The Excecutive is responsible towards the legislature. Ex.- Britain, India | There is a complete separation of powers between the excecutive and the legislature. Ex.- U.S.A |
6) Evolved Vs Enacted Constitution
| Evolved | Enacted |
| The Constitution has evolved over the years. It has not been drafted specifically. Ex.- British | A special constituent assembly is convened for framing the constitution. Ex.- U.S.A, India |
Constitutionalism
- It is the doctrine which entails that there should be limited government and rule of law shall be followed.
- The foundations of constitutionalism are based on the principle of supermacy of constitution, separation of powers, rule of law and independent judiciary.
- If the constitutionalism is followed then the rights of the citizens are secured and the accountability of the government is ensured.
Features associated with Constitutionalism
- Limited Government
- The government should run within the limits of the constitution.
- If the government is not limited then misuse of powers will occurred and there will be dictatorship.
- Separation of powers
- Checks & balances will be there.
- Independent Judiciary
- Transparancy & Accountability
Threats to the constitutionalism
- Concentration of powers
- It will promote misuse of power and authoritarianism.
- Concentration of power means the powers are not devolved with other authorities.
- If the govt. enjoys absolute majority in Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha then the govt. will have concentration of powers in their hand.
- If there is a weak opposition then the government may become unaccountable.
- Corruption
- Violation of Fundamental rights
- If judiciary is corrupt
- Election Malpractices
