Introduction
The Age of Mahajanapadas (6th Century BC) marks a turning point in ancient Indian history. This period witnessed the rise of 16 powerful territorial states, known as Mahajanapadas, leading to the decline of tribal political structures and the emergence of organized kingdoms and republics.
For BPSC aspirants, this topic is extremely important because three Mahajanapadas—Anga, Vajji, and Magadha—were located in Bihar, making it a favourite area for both Prelims and Mains.
What were Mahajanapadas?
- The term Mahajanapada means great territorial state.
- By 500 BC, 16 Mahajanapadas emerged.
- Geographical extent:
Indo-Gangetic plains from Afghanistan to Bengal and parts of Maharashtra - Political forms:
- Monarchies (Rajya)
- Republics (Gana-Sangha)
📌 This phase is associated with:
- Second Urbanisation
- Spread of Buddhism and Jainism
- Use of iron technology
List of 16 Mahajanapadas (Quick Revision)
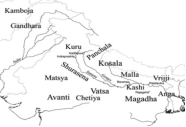
| Mahajanapada | Capital | Present Region |
|---|---|---|
| Anga | Champa | Eastern Bihar |
| Magadha | Rajgriha / Pataliputra | Central-South Bihar |
| Kashi | Varanasi | Uttar Pradesh |
| Vatsa | Kaushambi | Uttar Pradesh |
| Vajji | Vaishali | North Bihar |
| Kosala | Shravasti | Uttar Pradesh |
| Avanti | Ujjain | Madhya Pradesh |
| Malla | Kushavati | Uttar Pradesh |
| Panchala | Ahichhatra | Uttar Pradesh |
| Chedi | Shaktimati | UP–MP |
| Kuru | Indraprastha | Delhi–Haryana |
| Matsya | Virat Nagar | Rajasthan |
| Kamboja | Hataka | NW India |
| Shurasena | Mathura | Uttar Pradesh |
| Ashmaka | Potana | Deccan |
| Gandhara | Takshashila | Pakistan |
Mahajanapadas in Bihar (Most Important for BPSC)
1. Anga Mahajanapada
- Capital: Champa (earlier name: Malini)
- Region: Bhagalpur–Munger (Eastern Bihar)
- First mentioned in: Atharvaveda
- Associated with: Karna (Mahabharata)
- First King: Titikshu
- Annexed by: Bimbisara of Magadha
- Last ruler: Brahmadatta
📌 Exam Tip: Anga is listed as the 16th Mahajanapada in Anguttara Nikaya
2. Vajji (Vriji) Mahajanapada – A Republican State
- Capital: Vaishali
- Type: Republic (Gana-Sangha)
- Confederation of 8 tribes, including:
- Lichchhavi
- Jnatrika
- Videha
- Most powerful tribe: Lichchhavi
- Considered the first republic of the world
- Conquered by: Ajatashatru
📌 Panini referred to Vajji as “Vriji”
3. Vaishali – Capital of Lichchhavi Republic
- Located north of river Ganga
- Named after King Vishal
- Major centre of Buddhism and Jainism
- Birthplace of Lord Mahavira (Kundagram)
- King Chetaka was a powerful ruler
- His daughter Chellana married Bimbisara
📌 Mentioned in:
- Mahaparinibbana Sutta
- Arthashastra of Kautilya
4. Videha (Mithila)
- Region: North Bihar and Terai region of Nepal
- Capital: Janakpur
- Founder: Nimi Videh
- Raja Janaka was the most famous ruler
- Sita, wife of Lord Rama, belonged to Videha
- First mentioned in Yajurveda
5. Jnatrika Clan
- Clan of Lord Mahavira
- His father was the head of Jnatrika clan
- His mother was a Lichchhavi princess
- Shows political alliances through marriage
Magadha: The Most Powerful Mahajanapada
- Region: Patna and Gaya
- Founder: Brihadratha
- Famous ruler: Jarasandha
- Capital:
- Rajgriha (surrounded by 5 hills)
- Later shifted to Pataliputra
- Birthplace of:
- Mauryan Empire
- Gupta Empire
Reasons for the Rise of Magadha
- Fertile alluvial soil
- Availability of iron ore
- Dense forests
- Strategic location on river routes
📌 Magadha is first mentioned in Atharvaveda
Importance of Mahajanapadas for BPSC Prelims
Frequently Asked Areas:
- Mahajanapadas located in Bihar
- Capitals and founders
- Republican states
- Buddhist and Jain associations
- Anga–Magadha conflict
Importance for BPSC Mains (GS Paper-I)
Answer Writing Value:
- Rise of state system in ancient India
- Evolution from tribes to kingdoms
- Role of republics like Vajji
- Bihar as centre of early political development
📌 Mains Tip: Always highlight Bihar’s contribution to early Indian polity.
Map-Based Questions for BPSC
Practice marking:
- Anga – Bhagalpur, Munger
- Magadha – Rajgir, Patna
- Vaishali – Hajipur region
- Videha – Mithila (Darbhanga, Madhubani)
- Rivers: Ganga, Son, Gandak
Conclusion
The Age of Mahajanapadas laid the foundation of political unification, urbanisation, and religious reform movements in ancient India. Bihar played a central role in this transformation through Anga, Vajji, and Magadha, making this topic indispensable for BPSC Prelims and Mains.
